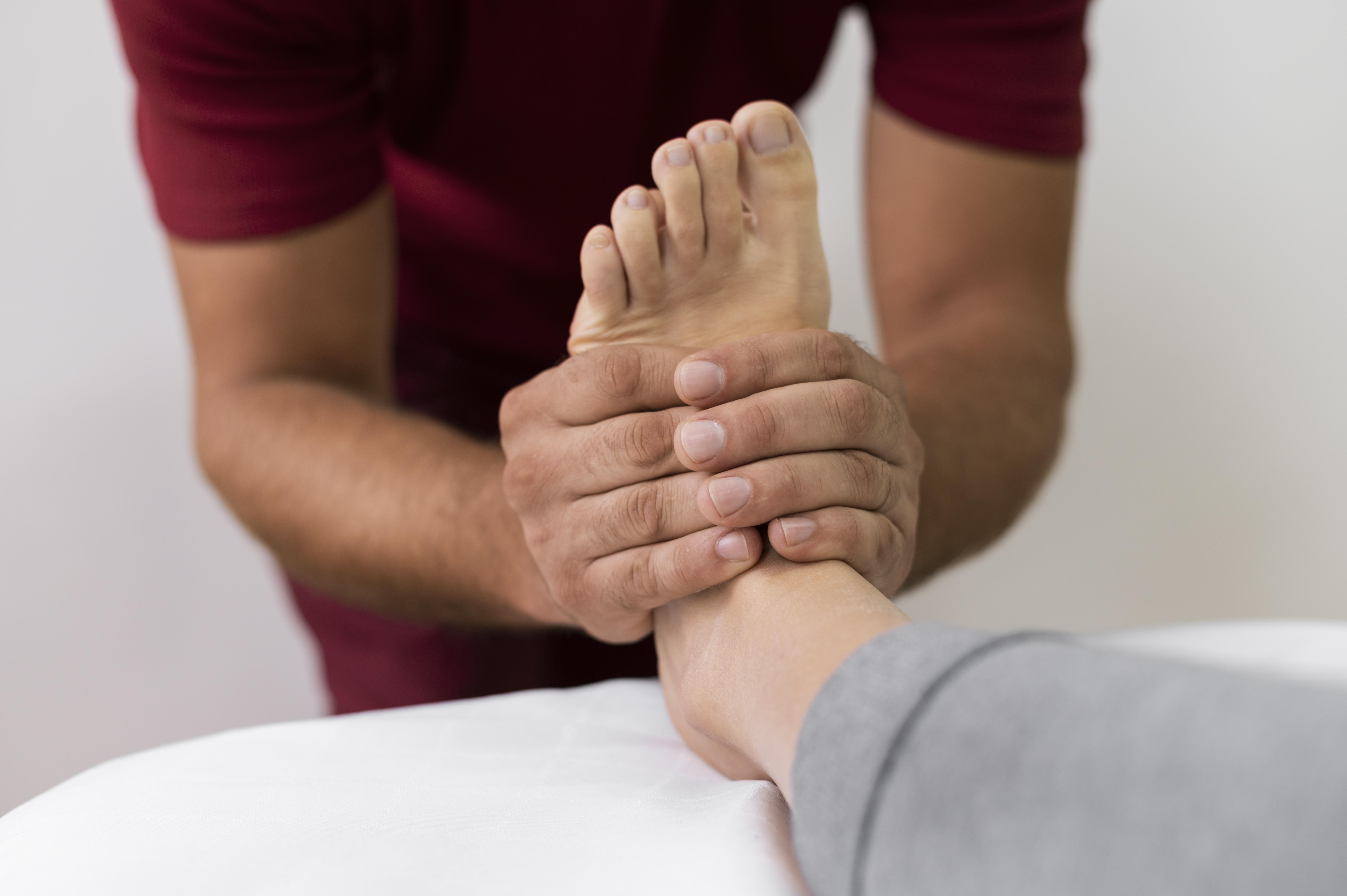

Fascia Foot
This modality focuses on movement, ROM, flexibility, holding positions like bending crouching lifting, etc. A series of manipulations and stretches encourage joint flexibility and muscular release. Good body mechanics allow you to distribute stress evenly throughout your body as you work. Otherwise, you may end up concentrating stress in one part of your body, making it more likely to injure the structures in that area. When you practise good body mechanics, you align your body in a posture that places the least amount of stress on your musculoskeletal system.
Your movements stay within a comfortable range around this neutral position. Working in this way, you can use the strength and momentum of your entire body to create movement, rather than using the smaller, more fragile parts of your body that are more easily injured. When your body moves as a unified whole, your movements can be more flowing, relaxed, even and controlled. The following techniques are employed to encourage and aid good body mechanics:-
Static stretching which attempts to alleviate excessively hypertonic (tight) muscles.
PNF stretches proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation are used in an attempt to decrease the tone in a muscle or muscle group that is assessed as being hypertonic or tight.To treat DOMS (delayed onset muscle soreness)
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) is typically used.
The use of very light muscular contractions, in very specific directions, is muscle energy techniques MET .This technique addresses joint restriction and joint ROM by altering the length of local musculature.
Benefits:
- Less tension on natural holding patterns
- Flexion and extension of musculature of foot
- Improved circulation
- Reduces edema
- Alleviates plantar fasciitis
- Helps prevent foot and ankle injuries
- Promotes better sleep
- Reduces inflammation
- Improves immunity
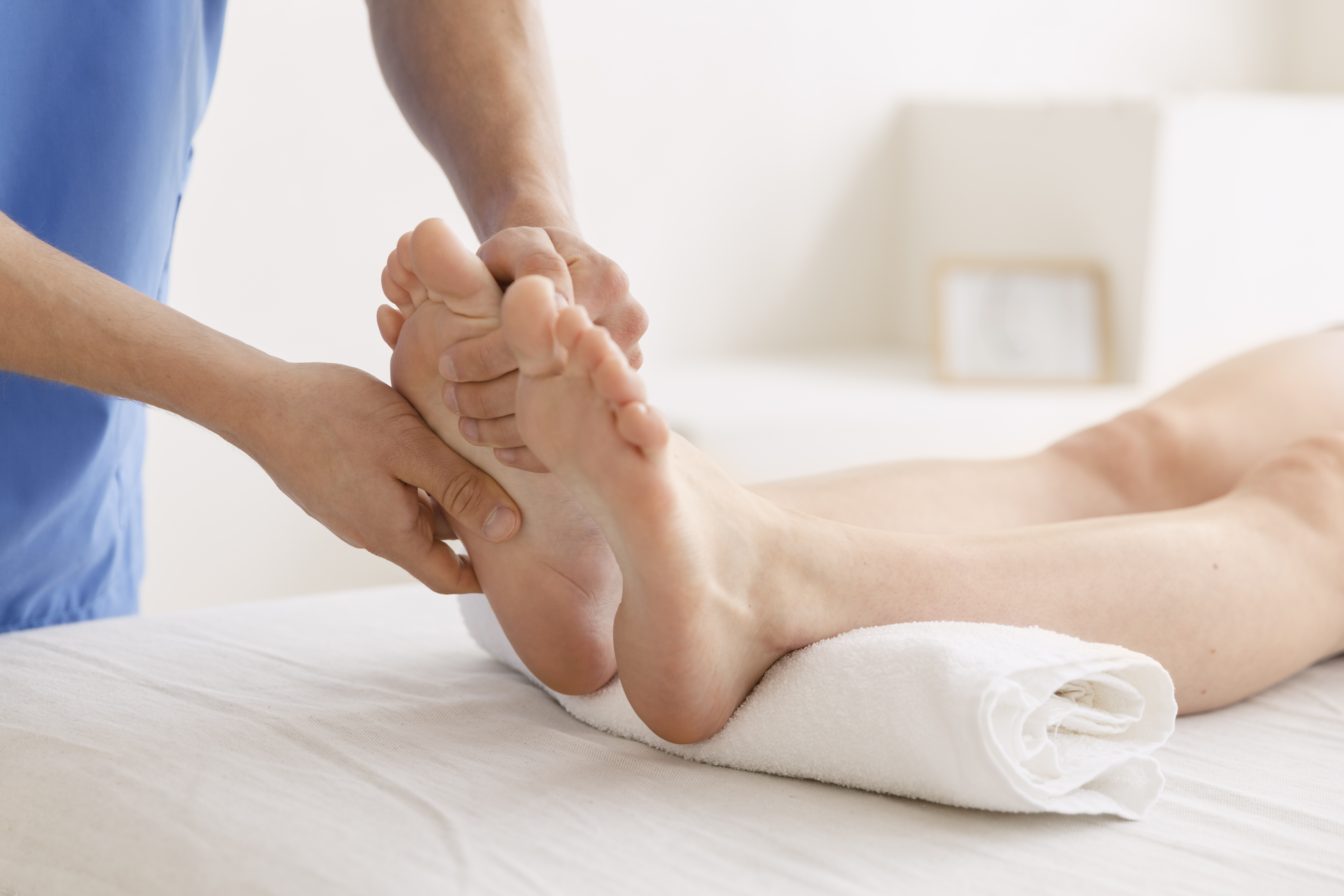

Fascia Foot

Thai Indian Massage